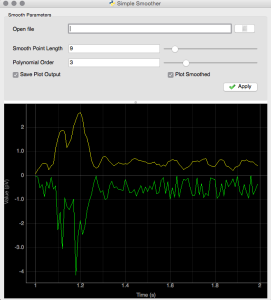
In an effort to create a set of simple tools that are useful for data processing and realtime analysis of data we’ve been exploring a range of tools. Granted there are a number of canned solutions in existence (e.g. National Instruments), however, to avoid the long-term challenges of compatibility we are looking for tools that can better serve our research goals. Two packages that we’ve began to lean more heavily upon include pyqtgraph and guidata. Both use PyQt4 and are compatible with Pyside for GUI rendering and construction. Matplotlib is quite mature but it has been our experience that pyqtgraph is quite a bit faster for plotting data in realtime.
The code below integrates pyqtgraph directly into the guidata framework. This is not a huge stretch as the pyqtgraph widgets integrate directly with the QWidget class in PyQt4. For those looking for an example the following code illustrate very simply how to integrate one of these plots and update it using simulated data along with the ability to alter the smoothing parameters of the raw data on the fly. One might envision the use of this approach to capture data from a streaming device (more on that later). It should be noted that the file loading feature has been disabled but it would’t be a huge stretch to re-enable this functionality for single spectra.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# Adapted from guidata examples:# Copyright © 2009-2010 CEA# Pierre Raybaut# Licensed under the terms of the CECILL License# (see guidata/__init__.py for details)# Adapted by Brian Clowers brian.clowers@wsu.edu"""DataSetEditGroupBox and DataSetShowGroupBox demoThese group box widgets are intended to be integrated in a GUI applicationlayout, showing read-only parameter sets or allowing to edit parameter values."""SHOW = True # Show test in GUI-based test launcherimport tempfile, atexit, shutil, datetime, numpy as Nfrom guidata.qt.QtGui import QMainWindow, QSplitterfrom guidata.qt.QtCore import SIGNAL, QTimerfrom guidata.qt import QtCorefrom guidata.dataset.datatypes import (DataSet, BeginGroup, EndGroup, BeginTabGroup, EndTabGroup)from guidata.dataset.dataitems import (FloatItem, IntItem, BoolItem, ChoiceItem, MultipleChoiceItem, ImageChoiceItem, FilesOpenItem, StringItem, TextItem, ColorItem, FileSaveItem, FileOpenItem, DirectoryItem, FloatArrayItem, DateItem, DateTimeItem)from guidata.dataset.qtwidgets import DataSetShowGroupBox, DataSetEditGroupBoxfrom guidata.configtools import get_iconfrom guidata.qthelpers import create_action, add_actions, get_std_icon# Local test import:from guidata.tests.activable_dataset import ExampleDataSetimport sys, osimport pyqtgraph as PG#-----------------------------------def simpleSmooth(fileName, polyOrder, pointLength, plotSmoothed = False, saveSmoothed = True): if not os.path.isfile(fileName): return False rawArray = get_ascii_data(fileName) #savitzky_golay(data, kernel = 11, order = 4) smoothArray = savitzky_golay(rawArray, kernel = pointLength, order = polyOrder) if plotSmoothed: plot_smoothed(smoothArray, rawArray, True) if saveSmoothed: newFileName = fileName.split(".")[0] newFileName+="_smth.csv" N.savetxt(newFileName, smoothArray, delimiter = ',', fmt = '%.4f') return smoothArray#-----------------------------------def get_ascii_data(filename): data_spectrum=N.loadtxt(filename,delimiter = ',', skiprows=0)##remember to change this depending on file format return data_spectrum#-----------------------------------def savitzky_golay(data, kernel = 11, order = 4): """ applies a Savitzky-Golay filter input parameters: - data => data as a 1D numpy array - kernel => a positive integer > 2*order giving the kernel size - order => order of the polynomal returns smoothed data as a numpy array invoke like: smoothed = savitzky_golay(<rough>, [kernel = value], [order = value] From scipy website """ try: kernel = abs(int(kernel)) order = abs(int(order)) except ValueError, msg: raise ValueError("kernel and order have to be of type int (floats will be converted).") if kernel % 2 != 1 or kernel < 1: raise TypeError("kernel size must be a positive odd number, was: %d" % kernel) if kernel < order + 2: raise TypeError("kernel is to small for the polynomals\nshould be > order + 2") # a second order polynomal has 3 coefficients order_range = range(order+1) half_window = (kernel -1) // 2 b = N.mat([[k**i for i in order_range] for k in range(-half_window, half_window+1)]) # since we don't want the derivative, else choose [1] or [2], respectively m = N.linalg.pinv(b).A[0] window_size = len(m) half_window = (window_size-1) // 2 # precompute the offset values for better performance offsets = range(-half_window, half_window+1) offset_data = zip(offsets, m) smooth_data = list() # temporary data, with padded zeros (since we want the same length after smoothing) #data = numpy.concatenate((numpy.zeros(half_window), data, numpy.zeros(half_window))) # temporary data, with padded first/last values (since we want the same length after smoothing) firstval=data[0] lastval=data[len(data)-1] data = N.concatenate((N.zeros(half_window)+firstval, data, N.zeros(half_window)+lastval)) for i in range(half_window, len(data) - half_window): value = 0.0 for offset, weight in offset_data: value += weight * data[i + offset] smooth_data.append(value) return N.array(smooth_data)#-----------------------------------def first_derivative(y_data): """\ calculates the derivative """ y = (y_data[1:]-y_data[:-1]) dy = y/2#((x_data[1:]-x_data[:-1])/2) return dy#-----------------------------------class SmoothGUI(DataSet): """ Simple Smoother A simple application for smoothing a 1D text file at this stage. Follows the KISS principle. """ fname = FileOpenItem("Open file", ("txt", "csv"), "") kernel = FloatItem("Smooth Point Length", default=7, min=1, max=101, step=2, slider=True) order = IntItem("Polynomial Order", default=3, min=3, max=17, slider=True) saveBool = BoolItem("Save Plot Output", default = True) plotBool = BoolItem("Plot Smoothed", default = True).set_pos(col=1) #color = ColorItem("Color", default="red") #-----------------------------------class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): QMainWindow.__init__(self) self.setWindowIcon(get_icon('python.png')) self.setWindowTitle("Simple Smoother") # Instantiate dataset-related widgets: self.smoothGB = DataSetEditGroupBox("Smooth Parameters", SmoothGUI, comment='') self.connect(self.smoothGB, SIGNAL("apply_button_clicked()"), self.update_window) self.fileName = '' self.kernel = 15 self.order = 3 self.pw = PG.PlotWidget(name='Plot1') self.pw.showGrid(x=True, y = True) self.p1 = self.pw.plot() self.p1.setPen('g', alpha = 1.0)#Does alpha even do anything? self.p2 = self.pw.plot(pen = 'y') self.pw.setLabel('left', 'Value', units='V') self.pw.setLabel('bottom', 'Time', units='s') splitter = QSplitter(QtCore.Qt.Vertical, parent = self) splitter.addWidget(self.smoothGB) splitter.addWidget(self.pw) self.setCentralWidget(splitter) self.setContentsMargins(10, 5, 10, 5) # File menu file_menu = self.menuBar().addMenu("File") quit_action = create_action(self, "Quit", shortcut="Ctrl+Q", icon=get_std_icon("DialogCloseButton"), tip="Quit application", triggered=self.close) add_actions(file_menu, (quit_action, )) ## Start a timer to rapidly update the plot in pw self.t = QTimer() self.t.timeout.connect(self.updateData) self.t.start(1000) def rand(self,n): data = N.random.random(n) data[int(n*0.1):int(n*0.23)] += .5 data[int(n*0.18):int(n*0.25)] += 1 data[int(n*0.1):int(n*0.13)] *= 2.5 data[int(n*0.18)] *= 2 data *= 1e-12 return data, N.arange(n, n+len(data)) / float(n) def updateData(self): yd, xd = self.rand(100) ydSmooth = savitzky_golay(yd, kernel = self.kernel, order = self.order) if self.smoothGB.dataset.plotBool: self.p2.setData(y=ydSmooth, x = xd, clear = True) self.p1.setData(y=yd*-1, x=xd, clear = True) else: self.p1.setData(y=yd, x=xd, clear = True) self.p2.setData(y=[yd[0]], x = [xd[0]], clear = True) if self.smoothGB.dataset.saveBool: if os.path.isfile(self.fileName): newFileName = self.fileName.split(".")[0] else: newFileName = "test" newFileName+="_smth.csv" N.savetxt(newFileName, ydSmooth, delimiter = ',')#, fmt = '%.4f') def update_window(self): dataset = self.smoothGB.dataset self.order = dataset.order self.kernel = dataset.kernel self.fileName = dataset.fname if __name__ == '__main__': from guidata.qt.QtGui import QApplication app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) |
Comments are closed